OpenAI Gears Up for Business: How OpenAI developed a sales strategy for GPT-4
Reporters offered a behind-the-scenes look at OpenAI’s year-long effort to capitalize on its long-awaited GPT-4. The company built a sales team and courted corporate partners in advance of launching its latest large language model, The Information reported.
Reporters offered a behind-the-scenes look at OpenAI’s year-long effort to capitalize on its long-awaited GPT-4.
What’s new: The company built a sales team and courted corporate partners in advance of launching its latest large language model, The Information reported.
How it works: OpenAI hired a head of sales only last June, four years after shifting from nonprofit to for-profit. She and her team began signing up corporate customers soon after.
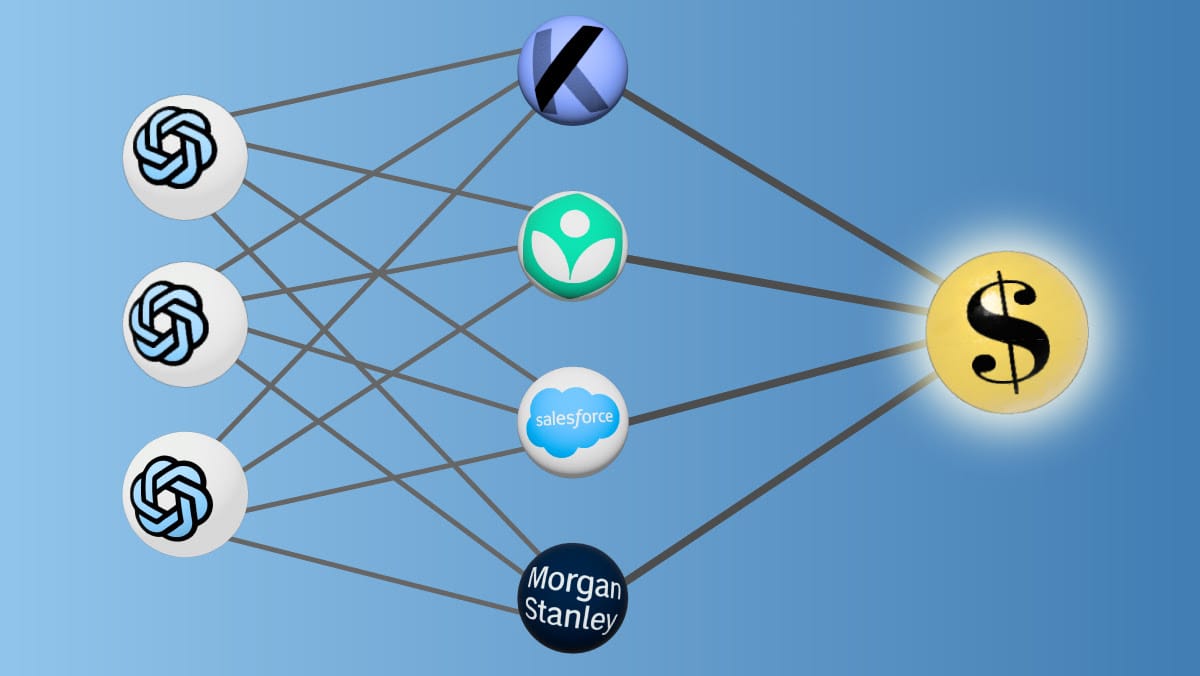
- The sales team offered access to the GPT-4 API along with engineers to assist in developing products based on it. Customers include Khan Academy, which uses ChatGPT to drive an educational chatbot; Morgan Stanley, which uses an unspecified model to query financial documents; and Salesforce, which uses OpenAI’s technology to power Einstein GPT, a service that crafts emails, analyzes sales data, and summarizes customer feedback.
- To Salesforce and product research startup Kraftful, the team sold access to servers that process large volumes of GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 prompts. Prices ranged from $264,000 a year for GPT-3.5 to $1.584 million a year for the most powerful version of GPT-4, according to a letter to prospective customers.
- OpenAI also helped customers develop customer-facing plugins that enable ChatGPT to surf the web and take advantage of third-party services. For instance, Expedia built a plug-in that tracks travel conversations to generate offers for flights, hotels, and holiday packages. Instacart developed one that enables customers to order groceries via prompt.
Path to profit: In 2015, OpenAI started as a nonprofit research lab dedicated to transparency. In 2019, it launched a profit-seeking subsidiary to fund its research. In a series of deals between 2019 and 2023, Microsoft invested upward of $13 billion in exchange for 49 percent of OpenAI’s profit and right of first refusal to commercialize its technology.
Yes, but: Observers have criticized both the company’s pivot to profit and its shift away from transparency. In a March interview, OpenAI’s co-founder Ilya Sutskever defended the organization’s secrecy, claiming it was necessary for safety as AI becomes more powerful.
Why it matters: OpenAI saw generative AI’s commercial potential before ChatGPT sparked investments around the globe. That foresight could pay off handsomely, as the company forecasted revenue of $200 million this year and $1 billion by 2024.
We’re thinking: OpenAI is building revolutionary technology that benefits hundreds of millions of users. We’re glad to see it on a path to financial sustainability.