Robotic Beehive For Healthier Bees: Beewise’s robotic beehive uses AI to save pollinators.
An automated beehive uses computer vision and robotics to help keep bees healthy and crops pollinated.
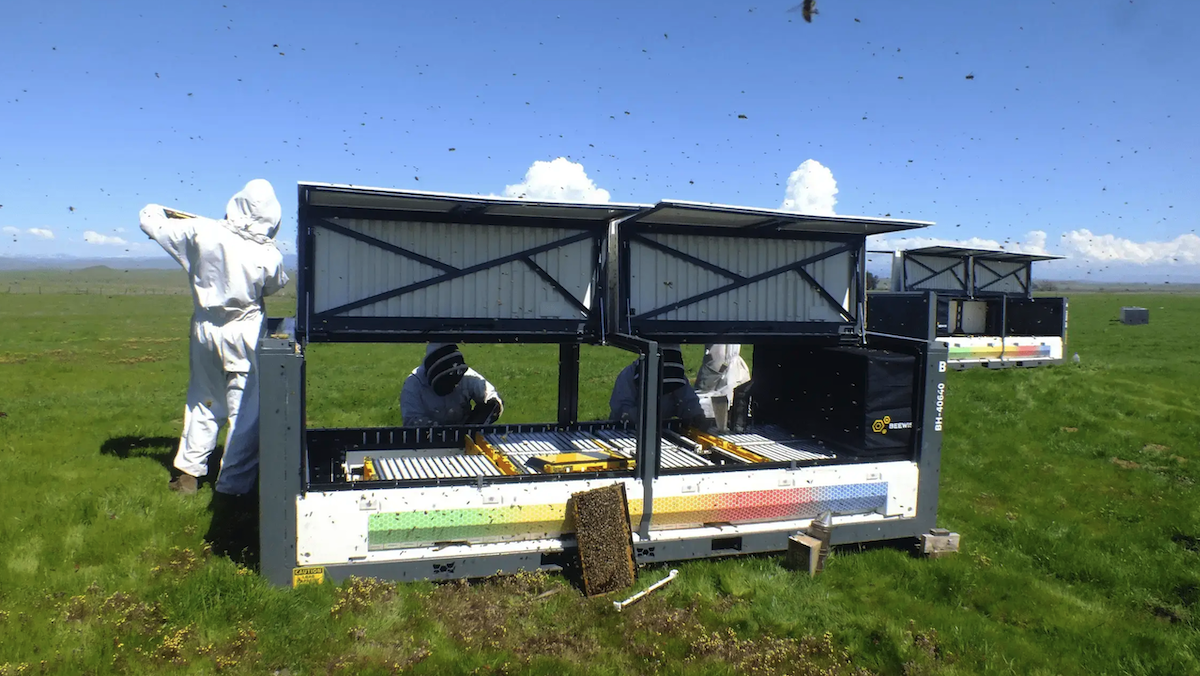

An automated beehive uses computer vision and robotics to help keep bees healthy and crops pollinated.
What’s new: The Beewise BeeHome 4 is a high-tech hive that scans bee colonies for parasites, hunger, and other adverse conditions, alerts beekeepers to them, and addresses some of them automatically. Over 300,000 units are currently deployed in North America, enabling beekeepers to monitor their hives remotely and helping farmers raise almonds, avocados, canola, coffee, cotton, and other crops that require pollination. While environmental stresses are killing bee colonies at an average rate of 40 percent per year over the last decade — rising to 62 percent in the U.S. last year — Beewise claims that its AI-enabled hive cuts that rate to 8 percent annually.
How it works: Around 11 feet long and covered with solar panels, the BeeHome 4 contains a robotic scanner, outfitted with cameras and grippers, that moves across the unit on rails. Nvidia Jetson and Raspberry Pi computers analyze the camera output, while sensors track the condition of the hive. Beekeepers can monitor conditions remotely and receive alerts to important changes via email or text message. Each unit holds up to 10 hives, each made up of 15 removable brood frames where bees build honeycombs to gestate larvae and store honey and pollen.
- A robot arm can lift each brood frame into the view of a system of cameras for analysis.
- Computer-vision models examine the photos to recognize conditions that affect the hive’s health. For instance, if the brood frames are full of honey, the system will alert the beekeeper. If the quantity of honey and pollen indicates that the bees should be fed, the robot fills a feeder with nutrients. If mites are detected, it moves the affected frame to a warming compartment that raises the temperature 2 degrees Fahrenheit, which kills 99 percent of the mites without harming the bees.
- Sensors track internal temperature and humidity and open and close the unit’s vents accordingly. If a sensor detects a pesticide or other harmful substances, the unit can close its vents.
- A GPS transmitter/receiver tracks the unit’s location and alerts the beekeeper if the unit is moved. The unit notifies the company and beekeeper in case of a malfunction.
Behind the news: Around 75 percent of flowering plants can’t bear fruit without pollination, so commercial beekeepers shuttle 2.5 million hives throughout the U.S. to keep farms productive. Yet the wooden Langstroth hive design was patented in 1852 and has changed little since then. Beewise built its initial prototype in 2018 using a GoPro camera. Two years later, it housed its first commercial units in 20-foot shipping containers. Debuted in 2023, the BeeHome 4 can be transported by a forklift and accommodates standard-sized brood frames.
Why it matters: Growers and beekeepers around the world are searching for ways to prevent colony collapse, the term that describes sudden die-offs of beehives that began in the 1980s. The causes are not fully understood but appear to include climate change, disease-carrying mites, and pesticides. Beekeepers typically check their hives’ health on a schedule of several weeks, but colonies can collapse much faster. AI-driven insights into hives’ health can help beekeepers to discover problems in time to save them, and robotic actions such as killing mites by heat can stave off potentially catastrophic threats automatically.
We’re thinking: AI is giving us healthier bees and more honey. Sweet!